Contents
The Rise of Corn Starch Food Container: A Sustainable Revolution in the Industry
Introduction to Corn starch food container
In recent years, the global push towards sustainability has significantly impacted various industries, including the food packaging sector. As concerns about environmental degradation and plastic pollution escalate, there is a growing need for innovative and eco-friendly alternatives. One such alternative gaining traction is cornstarch-based food packaging. This revolutionary approach has the potential to address some of the major challenges posed by traditional packaging materials, offering a more sustainable and environmentally friendly solution.
Corn starch food container takeaway food packaging has emerged as a sustainable alternative in the realm of eco-friendly materials. Derived from corn, this innovative packaging solution offers a biodegradable and renewable option for businesses looking to reduce their environmental footprint.

The Problem with Traditional Packaging:
Traditional food packaging, particularly single-use plastics, has become a significant environmental concern. Plastics take centuries to decompose, contributing to pollution in landfills, oceans, and ecosystems. Additionally, the production of plastic packaging involves the use of fossil fuels, further exacerbating the environmental impact.
Cornstarch as a Viable Alternative:
Corn starch food container packaging presents an exciting alternative to traditional materials. Derived from corn kernels, cornstarch is a renewable and abundant resource. The process of extracting cornstarch is relatively simple and energy-efficient, making it a sustainable option from the outset.
Key Advantages of Corn starch food Container:
- Biodegradability: Cornstarch-based packaging is biodegradable, meaning it can break down naturally over time. Unlike traditional plastics that persist in the environment for centuries, cornstarch-based materials decompose into natural compounds, minimizing the long-term impact on ecosystems.
- Renewable Resource: Corn is a renewable resource that can be cultivated annually, providing a continuous and sustainable supply for packaging production. This contrasts with fossil fuels used in the production of traditional plastics, which are finite resources.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: The production of cornstarch-based packaging typically involves lower energy consumption compared to traditional plastics. This results in a reduced carbon footprint, contributing to the fight against climate change.
- Versatility: Cornstarch-based materials can be adapted to various packaging needs. From containers and trays to films and coatings, the versatility of cornstarch-based packaging allows it to replace a wide range of traditional plastic applications.

Challenges and Considerations:
While cornstarch-based packaging holds immense promise, it is essential to acknowledge the challenges and considerations associated with its widespread adoption:
- Water Sensitivity: Cornstarch-based materials can be sensitive to moisture, affecting their performance in certain conditions. Researchers are continually working to enhance the water resistance of these materials to make them suitable for a broader range of applications.
- Land Use for Corn Cultivation: The increasing demand for corn as a raw material for packaging raises concerns about potential land use changes and their environmental impact. Sustainable farming practices and responsible land management are crucial to mitigating these concerns.
- Cost Considerations: At present, cornstarch-based packaging may be slightly more expensive than traditional plastics. However, as technology advances and economies of scale come into play, the cost is expected to decrease, making it more economically viable for widespread adoption.
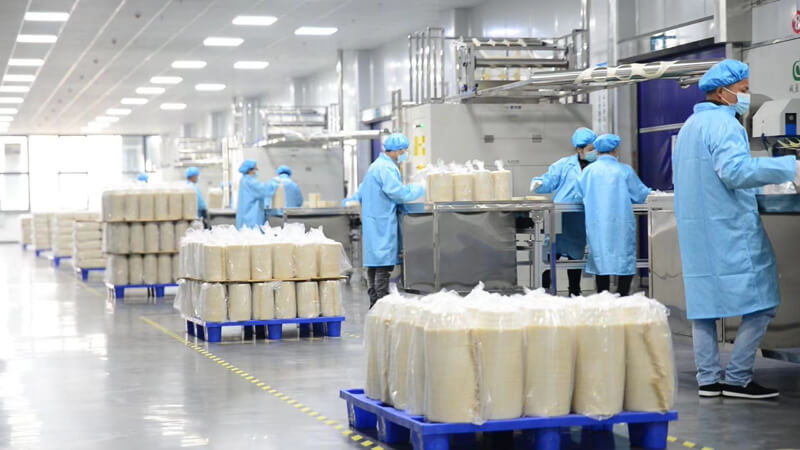
Production Process of Cornstarch Packaging
The production process of cornstarch packaging involves several key steps, from sourcing raw materials to the manufacturing of the final product. Here is an overview of the typical production process:
- Corn Cultivation and Harvesting: The process begins with the cultivation of corn. Corn is a versatile and widely grown crop that serves as the primary source of cornstarch. Farmers cultivate corn in large fields, and the crop is harvested once it reaches maturity.
- Corn Milling: After harvesting, the corn kernels are separated from the cob and then subjected to a milling process. Milling involves grinding the corn kernels into a fine powder to extract the starch. This starch is the key raw material for the production of cornstarch-based packaging.
- Starch Extraction: The milled corn undergoes a separation process to extract the starch. Typically, this involves washing the milled corn with water to separate the starch from other components, such as proteins and fibers. The resulting starch slurry is then processed to isolate the pure starch.
- Drying and Modification: The extracted starch is often in the form of a wet slurry, and it needs to be dried to obtain a stable powder. The drying process can vary, but it usually involves heating the starch to remove moisture. Additionally, the starch may undergo modification processes to enhance its properties, such as improving water resistance or increasing flexibility.
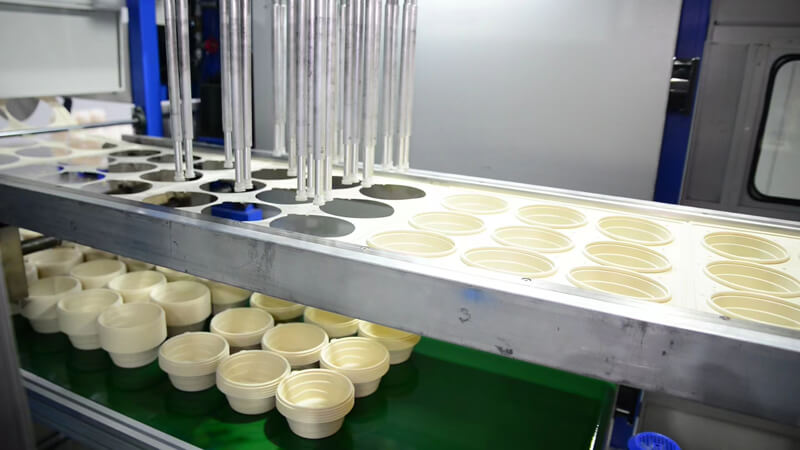
- Biopolymer Production: The modified cornstarch is then used to produce a biopolymer. This involves processing the starch through various chemical and mechanical methods to create a material with the desired characteristics for packaging applications. The resulting biopolymer can be in the form of pellets or sheets.
- Film Extrusion or Molding: The cornstarch-based biopolymer is then processed through extrusion or molding machines to form the desired packaging shape. In the case of films or coatings, the biopolymer can be extruded into thin sheets. For containers or other three-dimensional shapes, molding processes such as injection molding or thermoforming may be employed.
- Cooling and Solidification: Once the packaging shape is formed, it goes through a cooling and solidification process. This step is crucial for ensuring the stability and integrity of the final product. The cooling time and conditions may vary depending on the specific properties of the cornstarch-based material.
- Cutting and Finishing: After solidification, the cornstarch-based packaging is cut and finished to meet the desired specifications. This may involve trimming excess material, adding surface finishes, or incorporating additional features, depending on the intended use.
- Quality Control: Throughout the entire production process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the cornstarch packaging meets industry standards and specifications. This includes testing for factors such as strength, flexibility, and biodegradability.
- Packaging and Distribution: The finished corn starch food container is then packaged and prepared for distribution. Companies may choose to sell the packaging material directly to manufacturers or incorporate it into their packaging solutions for various products.
As technology continues to advance, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on optimizing each step of the production process to improve the performance and cost-effectiveness of cornstarch-based packaging.
Case Studies and Success Stories:
Several companies and initiatives have embraced cornstarch-based packaging, showcasing its feasibility and effectiveness:
- Eco-Friendly Brands: Numerous eco-conscious brands have adopted cornstarch-based packaging for their products. These brands prioritize sustainability and leverage cornstarch’s eco-friendly properties to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Food Industry Applications: In the food industry, corn starch food container have been successfully used for takeaway containers, cutlery, and other single-use items. Restaurants and food service providers are recognizing the importance of adopting sustainable packaging solutions to align with changing consumer preferences.
Lifecycle of Corn starch food container
Understanding the environmental impact of packaging is crucial. It emphasizes the eco-friendly attributes that make cornstarch containers a sustainable choice.
The lifecycle of corn starch food containers encompasses various stages, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal or recycling. Here’s a breakdown of the typical lifecycle of cornstarch containers:
- Raw Material Extraction: The lifecycle begins with the cultivation of corn, which serves as the primary raw material for cornstarch containers. Corn is grown, harvested, and processed to extract the starch. The starch undergoes further modification to create a biopolymer suitable for container production.
- Manufacturing of Cornstarch Containers: The processed cornstarch is then used to produce containers through molding processes like injection molding or thermoforming. The containers can take various shapes and sizes, depending on the intended application. The manufacturing stage involves shaping the cornstarch-based biopolymer into the final product.
- Distribution and Use: Once manufactured, cornstarch containers are distributed to various industries, including food service, packaging, and retail. These containers are used for packaging food products, beverages, and other goods. Consumers encounter cornstarch containers in various settings, from restaurants to grocery stores.
- End-of-Life Options: At the end of their use, cornstarch containers can follow different pathways based on their disposal or recycling options. The primary end-of-life options include:
- Biodegradation: Cornstarch containers are designed to be biodegradable. When exposed to the right conditions, such as moisture and microbial activity, they break down into natural compounds, reducing environmental impact.
- Composting: Cornstarch containers can be composted in industrial composting facilities or home composting systems. In a controlled composting environment, they break down more efficiently, contributing to nutrient-rich compost for soil.
- Landfill Disposal: If cornstarch containers end up in landfills where conditions for biodegradation are limited, their environmental benefits may be reduced. However, compared to traditional plastics, they are still likely to break down at a faster rate.
- Recycling: Some cornstarch-based materials may be recyclable, depending on the specific composition and local recycling facilities. Recycling processes for cornstarch containers can vary, and not all recycling facilities may accept them. Advances in technology may improve the recyclability of cornstarch-based materials over time.
- Biodegradation and Environmental Impact: Cornstarch containers, when exposed to natural conditions conducive to biodegradation, undergo a process where microorganisms break down the material into simpler components. This process is generally more environmentally friendly than the persistence of traditional plastics in the environment. It reduces the risk of long-term pollution and contributes to the natural nutrient cycle.
- Renewable Resource Management: As corn is a renewable resource, sustainable farming practices and responsible land management are crucial for ensuring the continued availability of the raw materials for cornstarch containers. Ethical and sustainable sourcing practices help mitigate potential environmental impacts associated with large-scale agricultural activities.
- Ongoing Research and Innovation: The lifecycle of cornstarch containers is subject to ongoing research and innovation. Scientists and manufacturers continually explore ways to improve the performance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact of cornstarch-based packaging materials. Advancements in technology may lead to enhanced properties and increased recyclability.
- Consumer Education: Throughout the lifecycle, educating consumers about the environmentally friendly aspects of cornstarch containers and proper disposal methods is essential. Consumer awareness contributes to responsible use, disposal, and recycling practices, ultimately enhancing the positive environmental impact of cornstarch containers.
The lifecycle of cornstarch containers highlights their potential as a more sustainable alternative to traditional plastic packaging. From renewable resource extraction to end-of-life considerations, the environmental benefits of cornstarch containers depend on responsible use, disposal, and ongoing efforts to improve their overall lifecycle impact.
Reasons to Adopt Corn Starch Food Container
The adoption of cornstarch packaging has gained momentum in recent years, driven by a range of environmental, economic, and consumer-related factors. Here are several compelling reasons for businesses and industries to consider adopting cornstarch packaging:
- Biodegradability: One of the primary reasons to adopt cornstarch packaging is its biodegradability. Unlike traditional plastics, which can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, cornstarch-based materials break down into natural compounds when exposed to the right conditions. This feature significantly reduces the long-term environmental impact associated with packaging waste.
- Renewable Resource: Corn, the source of cornstarch, is a renewable resource that can be cultivated annually. This contrasts with the finite nature of fossil fuels used in the production of traditional plastics. The use of renewable resources contributes to the overall sustainability of cornstarch packaging.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: The production of cornstarch-based packaging typically involves lower energy consumption compared to traditional plastics. The cultivation of corn and the extraction of cornstarch require less energy and result in a reduced carbon footprint. This aligns with global efforts to mitigate climate change and transition towards more sustainable practices.
- Versatility: Cornstarch-based materials are versatile and can be adapted to various packaging needs. From containers and trays to films and coatings, the versatility of cornstarch packaging allows it to replace a wide range of traditional plastic applications. This adaptability makes it an attractive option for businesses seeking eco-friendly alternatives across diverse industries.
- Consumer Preference for Sustainability: Consumer awareness and concern about environmental issues have grown significantly. Many consumers actively seek products with eco-friendly packaging, and adopting cornstarch packaging aligns with this shift in consumer preferences. Businesses that prioritize sustainability may enhance their brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the environmental impact of traditional plastics. As a response, there is a trend towards implementing regulations and policies that encourage or mandate the use of sustainable packaging materials. Adopting cornstarch packaging positions businesses to comply with evolving regulations and demonstrates corporate responsibility.
- Innovation and Technological Advancements: Ongoing research and technological advancements in the field of biodegradable materials contribute to the continuous improvement of corn starch food containers. Innovations in processing techniques, material modifications, and improved properties make cornstarch packaging an increasingly viable and effective alternative to traditional plastics.
- Waste Reduction and Circular Economy: Cornstarch packaging contributes to the concept of a circular economy by promoting waste reduction. The biodegradability and compostability of cornstarch-based materials support efforts to minimize the accumulation of non-recyclable waste in landfills. Additionally, cornstarch packaging can be part of a closed-loop system, where waste is repurposed as compost for agriculture.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Adopting cornstarch packaging aligns with corporate social responsibility goals. Businesses that integrate sustainable practices into their operations, including the use of eco-friendly packaging, enhance their reputation and contribute to positive social and environmental outcomes.
- Market Differentiation: In a competitive market, adopting cornstarch packaging can serve as a unique selling point. Businesses that differentiate themselves by prioritizing sustainability may attract environmentally conscious consumers and gain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
The adoption of cornstarch packaging offers a range of benefits, from addressing environmental concerns to meeting consumer expectations and complying with regulatory requirements. As businesses increasingly recognize the importance of sustainable practices, cornstarch packaging emerges as a practical and eco-friendly solution for the packaging industry.
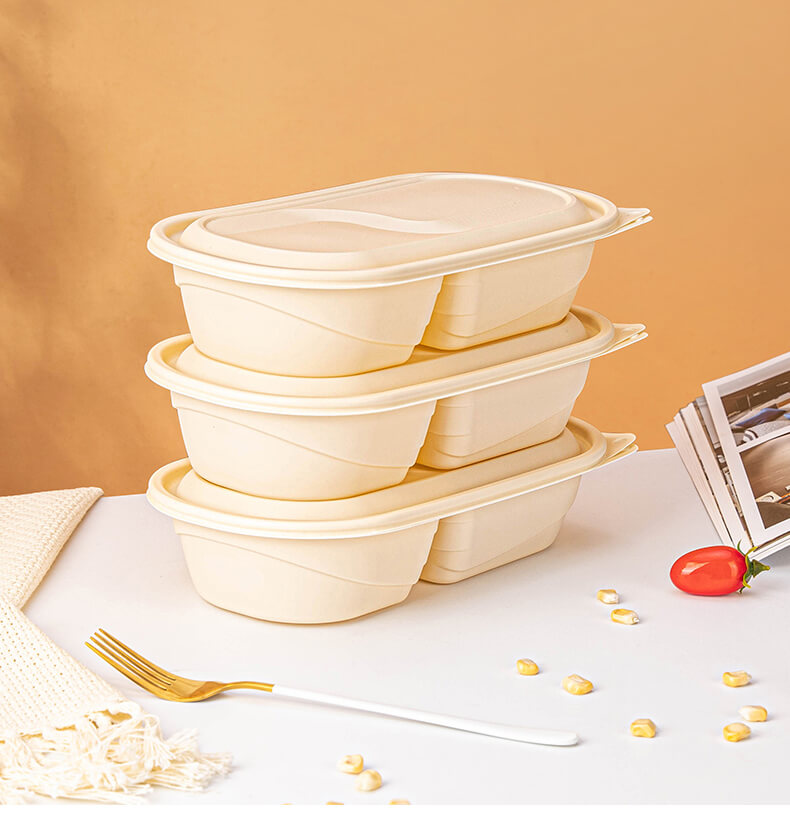

Conclusion:
Corn starch food container represents a promising step towards a more sustainable and eco-friendly future. As the world grapples with the environmental consequences of traditional packaging materials, the adoption of alternatives like cornstarch can play a pivotal role in mitigating these issues. While challenges exist, ongoing research and innovation are paving the way for improved cornstarch-based materials that meet the diverse needs of the food packaging industry. As consumer awareness grows and regulatory pressures increase, the transition to cornstarch-based packaging is likely to accelerate, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient planet.

 By Sofier Ju
By Sofier Ju


